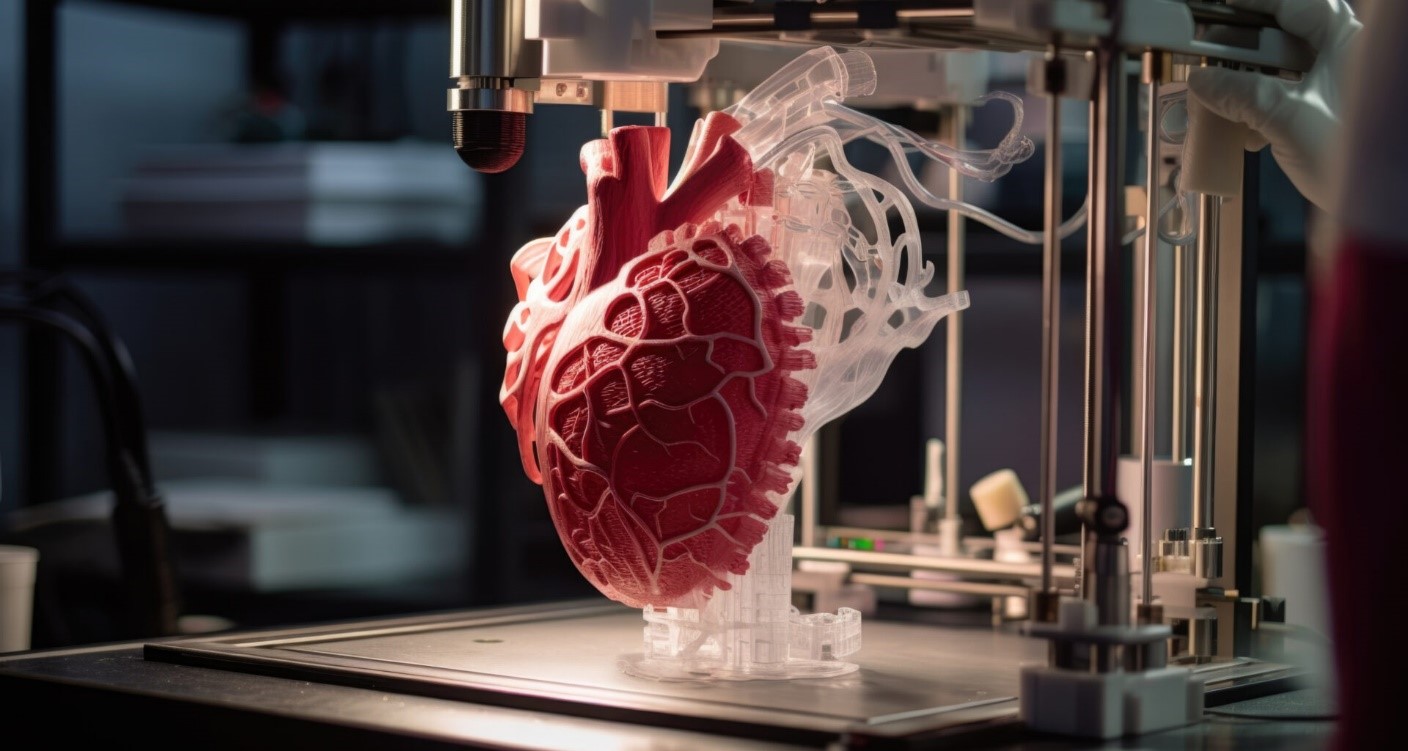
Organ 3-D Printing Evaluation
Organ 3D printing is one of the most promising technologies in the field of medicine as it could be a solution to the problem of the lack of donor organs. This new clinical strategy could replace damaged organs with new ones, created from biological materials to help patients with organ failure.

Here is the Process of Organ 3D Printing and Steps Followed:
1. The Scaffold creation: A 3D scaffold is known to be designed based on the specific organ’s structure and function. The scaffold provides a structure which new tissues are developed using.
2. Cell seeding: In this step the cells from the donor or patient are placed on the scaffold. The cells later on develop into the organ.
3. Bioprinting: the procedure of 3D printing is applied when layering cells and biomaterials to form the specific shape of the organ on the scaffold.
4. Maturation: Here the printed organ is then incubated in a bioreactor to gain maturation in order to perform the desired function.

Research has shown that the benefit resulting from the use organ 3D printing, is that the risk of rejection may decrease. Besides, do you know that by using the patient’s own cells, the immune system is likely to recognize the transplanted organs as foreign? The amazing thing is that 3D printing can build any organ well suited to the individual wishes therefore improving chances of successful transplantation.
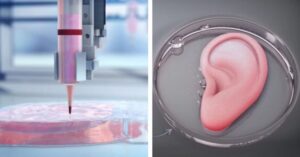
Do you know that although organ 3D printing is still in its early years, there is already much progress? It has been put to use by scientists to develop tissues that are functional ones like blood vessels and skin and the rest. When it comes to the printing of organs like hearts and livers it is not easy because of the intricate structure, which bring with them added pressure of functional accuracy. Despite there being challenges in organ 3D printing, there is also many benefits.
PHOTO CREDIT: GOOGLE.COM
WRITTEN BY: AMEDICC.COM